What is a home care agency? A home care agency is a business that provides non-medical support and assistance to individuals in their own homes. This can include help with daily living activities, companionship, and household tasks. Can I start a home care agency with no experience? Yes, with thorough research, a solid business plan, and the right team, you can launch a successful home care business even without prior industry experience. Who is the target market for a home care agency? The primary target market is typically seniors who wish to age in place, but it also includes individuals recovering from illness or surgery, those with disabilities, and people needing respite care.
Starting a home care business requires careful planning and dedication. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to launch your own agency for care at home, from initial concept to ongoing operations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to build a reputable and thriving enterprise.
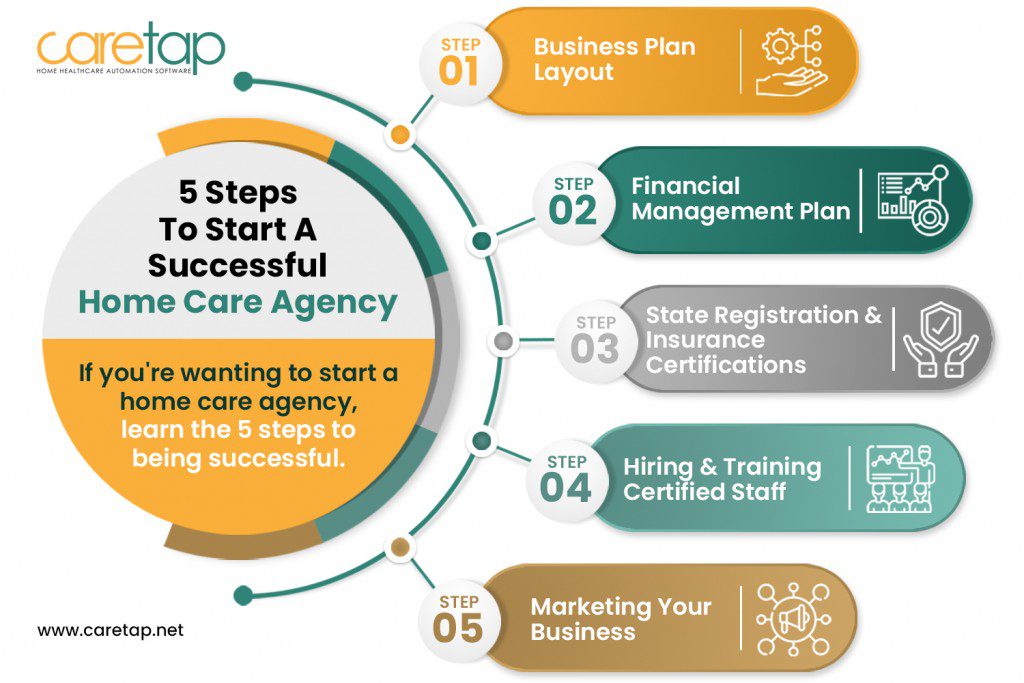
Image Source: caretap.net
Laying the Foundation: Your Caregiving Business Plan
A well-structured caregiving business plan is the bedrock of your home care agency. It’s not just a document; it’s your roadmap to success. This plan should clearly outline your vision, mission, and the specific services you intend to offer. It will also be crucial for securing funding and attracting potential investors or partners.
Defining Your Niche and Services
Consider what specific in-home care services you will provide. Will you focus on general elder care, specialized conditions like dementia or Alzheimer’s, post-operative recovery, or perhaps disability support? Offering specialized services can help you stand out in a competitive market.
Common private duty home care services include:
- Personal Care: Assistance with bathing, dressing, grooming, toileting, and feeding.
- Companionship: Social interaction, conversation, and engagement in activities.
- Household Tasks: Light housekeeping, laundry, meal preparation, and errands.
- Medication Reminders: Ensuring clients take their medications as prescribed.
- Transportation: Accompanying clients to appointments or social outings.
- Respite Care: Providing temporary relief for family caregivers.
- Specialized Care: Support for individuals with chronic illnesses, cognitive impairments, or disabilities.
Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Before you dive in, thoroughly research your local market. Identify the demographics of your target population and the existing elderly care agency providers. What are their strengths and weaknesses? What gaps exist in their service offerings? This research will inform your unique selling proposition.
Financial Projections and Funding
Your business plan must include detailed financial projections. Estimate your startup costs, operating expenses, and revenue streams. Determine how you will fund your home care business startup, whether through personal savings, loans, or investors.
Key financial considerations include:
- Startup Costs: Licensing, insurance, office space (if applicable), equipment, initial marketing, and legal fees.
- Operating Expenses: Salaries and wages for caregivers and administrative staff, insurance premiums, marketing, supplies, and ongoing training.
- Pricing Strategy: How will you price your services competitively while ensuring profitability?
Navigating the Legal and Administrative Landscape
Establishing a legal entity and complying with all regulations is paramount for a home care agency. This ensures you operate ethically and avoid legal repercussions.
Business Registration and Legal Structure
Choose a legal structure for your business, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation. Register your business name with the appropriate government agencies. Consult with a legal professional to ensure you establish the correct structure and comply with all local, state, and federal laws.
Home Care Licensing and Certifications
Home care licensing requirements vary significantly by state. Some states require specific licenses for home care agencies, while others have fewer regulations for non-medical providers. It is vital to research and obtain all necessary licenses and certifications to operate legally. This might include:
- State Business License: Standard for all businesses.
- Home Care Agency License: Specific to the industry, often requiring background checks, insurance, and proof of a business plan.
- Background Checks: For all employees, ensuring client safety.
- Liability Insurance: To protect your business from potential claims.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: To cover employees injured on the job.
Failing to meet these requirements can result in hefty fines or even the closure of your business.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Even for non-medical agencies, understanding relevant healthcare regulations is important. This includes adhering to privacy laws like HIPAA, although direct HIPAA compliance is more stringent for agencies providing skilled nursing or therapy. Familiarize yourself with elder abuse reporting requirements in your state.
Building Your Team: Recruiting and Managing Home Caregivers
Your caregivers are the heart of your home care agency operations. They are the ones directly providing care, so their quality, reliability, and compassion are critical to your success.
The Recruitment Process
Developing a robust recruitment strategy is essential for finding qualified and compassionate individuals. Look for candidates with empathy, patience, strong communication skills, and a genuine desire to help others.
Key steps in recruitment:
- Job Postings: Utilize online job boards, local community centers, and nursing schools.
- Application Screening: Review resumes and applications for relevant experience and qualifications.
- Interviews: Conduct thorough interviews, including behavioral questions, to assess personality and suitability for caregiving.
- Background Checks: Perform comprehensive criminal background checks and verify references.
Training and Professional Development
Invest in ongoing training for your caregivers. This ensures they are up-to-date on best practices, understand specific client needs, and are proficient in their duties. Training programs can cover:
- Caregiving Techniques: Proper lifting, transferring, and assisting with daily living activities.
- First Aid and CPR: Essential life-saving skills.
- Specialized Care Training: Dementia care, fall prevention, and medication management.
- Client Rights and Dignity: Emphasizing respectful and person-centered care.
- Emergency Procedures: How to respond in various situations.
Compensation and Retention
Fair compensation and a positive work environment are crucial for retaining your valuable caregivers. Offer competitive wages, benefits (if feasible), and opportunities for career advancement. Recognize and reward exceptional performance to boost morale and reduce turnover.
Setting Up Your Operations: The Back Office
Efficient home care agency operations require a well-organized administrative system. This includes client management, scheduling, billing, and record-keeping.
Client Intake and Assessment
Develop a standardized process for client intake and assessment. This involves gathering comprehensive information about the client’s medical history, care needs, preferences, and home environment. A thorough assessment allows you to create a personalized care plan.
Scheduling and Coordination
Effective scheduling is vital to ensure clients receive consistent care. Utilize scheduling software to manage caregiver availability, client appointments, and track hours worked. Clear communication with both clients and caregivers is key to preventing missed visits or scheduling conflicts.
Billing and Payroll
Establish a clear billing system to invoice clients accurately and on time. This may involve working with insurance providers, long-term care policies, or private pay clients. Implement a reliable payroll system to ensure caregivers are paid accurately and promptly.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
Maintain meticulous records for all clients and caregivers. This includes care plans, visit notes, incident reports, and time sheets. Proper documentation is crucial for continuity of care, legal compliance, and quality assurance.
Marketing Your Home Care Business: Reaching Your Clients
Effective marketing a home care business is essential to attract clients and grow your agency. You need to build trust and awareness within your community.
Building a Strong Brand Identity
Develop a professional brand identity that reflects your agency’s values and commitment to quality care. This includes your logo, website, and marketing materials.
Online Presence
A strong online presence is non-negotiable.
- Website: Create a user-friendly website that clearly outlines your services, your mission, and provides contact information. Include testimonials from satisfied clients to build credibility.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimize your website and content to rank higher in search engine results for terms like “home care services near me” or “elder care agency [your city].”
- Social Media Marketing: Engage with your community on social media platforms. Share helpful content, client success stories, and information about your services.
Community Outreach and Networking
Build relationships within your community.
- Local Healthcare Providers: Network with doctors, hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and elder care facilities. They can be valuable referral sources.
- Community Events: Participate in local health fairs, senior expos, and community events to increase visibility.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with senior living communities, churches, and other organizations that serve your target demographic.
Testimonials and Referrals
Encourage satisfied clients and their families to provide testimonials and referrals. Positive word-of-mouth is one of the most powerful marketing tools.
Table: Key Startup Tasks and Estimated Timeline
This table provides a general overview of the tasks involved in launching a home care agency and a potential timeline. Actual timelines may vary based on individual circumstances and local regulations.
| Task | Estimated Timeline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Business Plan Development | 1-2 Months | Involves market research, financial projections, and strategy. |
| Legal Structure & Registration | 1 Month | Registering the business and obtaining necessary legal documents. |
| Home Care Licensing & Permits | 2-6 Months | Varies significantly by state; research thoroughly. |
| Insurance Acquisition | 1 Month | General liability, professional liability, workers’ compensation. |
| Develop Caregiving Policies & Procedures | 1 Month | Client intake, care plans, emergency protocols, code of conduct. |
| Recruitment Strategy | Ongoing | Planning how to find and vet caregivers. |
| Office Setup (if applicable) | 1-2 Months | Securing space, furniture, technology. |
| Marketing Strategy Development | 1 Month | Branding, website, initial outreach plans. |
| Initial Caregiver Recruitment & Training | 1-2 Months | Hiring and onboarding the first cohort of caregivers. |
| Launch Operations | Target Date | Ready to accept clients and provide services. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are the biggest challenges when starting a home care agency?
A1: Some common challenges include intense competition, the cost of insurance and licensing, recruiting and retaining reliable caregivers, and managing operational complexities. Building a strong reputation and ensuring consistent quality of care are also ongoing efforts.
Q2: How much does it cost to start a home care agency?
A2: The cost can vary widely. Startup expenses can range from $10,000 to $50,000 or more, depending on your location, licensing requirements, insurance needs, and whether you opt for an office space versus a home-based operation initially.
Q3: What qualifications do home care agencies need for their caregivers?
A3: While specific requirements vary, most agencies look for caregivers with experience in caregiving, a high school diploma or GED, and certifications like CPR and First Aid. Thorough background checks and strong interpersonal skills are also essential.
Q4: How do home care agencies get clients?
A4: Clients are typically acquired through referrals from hospitals, doctors, rehabilitation centers, and elder care communities. Online marketing, community outreach, positive word-of-mouth, and strong relationships with healthcare professionals are also key.
Q5: Is it better to start a non-medical or medical home care agency?
A5: Starting a non-medical home care agency generally involves fewer regulatory hurdles and lower startup costs compared to a medical home health agency, which requires licensing as a healthcare provider and often employs licensed nurses and therapists. Many successful agencies begin as non-medical and may expand into medical services later.
Q6: What is the difference between home care and home health care?
A6: Home care typically refers to non-medical assistance with daily living activities, such as bathing, dressing, meal preparation, and companionship. Home health care, on the other hand, involves skilled medical services provided by licensed professionals, such as nurses or physical therapists, often ordered by a physician.
Launching a home care agency is a rewarding venture that allows you to make a significant positive impact on individuals and families. By meticulously planning, adhering to regulations, building a strong team, and effectively marketing your services, you can establish a successful and reputable home care business startup that provides much-needed in-home care services. Remember that dedication to quality and compassionate care will be your greatest assets.
